How to understand international politics
Date: 21-feb-2024
Conceptual framework to understand international politics
Q. What drives international politics
Ans. Capitalism
Nature of capitalism: expansionist
- Is always imperialist
- Militant
- Nationalist: nationalism is a ideology to legitimise a war
Since beginning of modern times we are living in the world of capitalism. Even origin of international politics begin with rise of modernity/capitalism.
Hence there are recurrent wars and struggles competition to acquire the region which are
- Full of natural resources
- Located at major trade routes
- Major markets
There are two framework to understand world politics
- Geopolitics : geopolitics has been the recurrent theme of foreign policy. Geopolitics reflect attempt to Physical control the market. physical control require the greater armed force. It means more battle and wars. more threat to peace / More militarization / More armed race
whether it is politics among european nations from 1648 till 2nd world war or super power Rivalry from the end of World War 2 to till 1991 world politics Is understood through geopolitics.
From 1991 to 2001, further from 2001 till 2007 (global financial crisis) and finally 2013 onwards we see 1st prominence of geo economics Means Integration of markets It does not require physical control, which is more cost intensive.
- Geo economics :
In geo economics khakis get replaced by grey suits, business executives become the soldiers.
This phase in international politics came to be described as globalisation however gradually geo economics started getting replaced by geo politics again. The reason was China's challenge to US hegemony
Hence USA return to geopolitics. Year 2001 US militarily entered Afghanistan. Stationed its forces in the heart of Asia. Wider central asia means which covers west asian peripheries (Iran, Turkey, covers caucas region) Which touches russia and southern Europe Adjacent to China South Asia and Turkey.
Thus, a place to control all of its regional rival.
Thus Gradually we see USA over stretching itself and regional powers not comfortable with us presence started working in greater tandem. There has been a phenomenal change in foreign policy with some of its allies for eg. turkey
Regional powers working in tandem played the role in exit in the US from Afghanistan. Exit of USA from Afghanistan Gives a clear indicator about decline of US and rise of multipolarity.
Every country in the region has started geopolitics in the new gar of geo economics. Starting with
- China's BRI , which is understood as China's land grab.
- Russia revanchism(Attempt to get the old land), means gaining control over historical land, for eg. Georgia and Ukraine.
- Turkey new aspiration to re-establish Itself in the place of historical Ottoman Empire Reflected in the Turkey new approach to foreign policy(More activism more pro Asia)(If not anti west)
Turkey changing its official name turkey to turkiye(i.e. The Republic of Turkey).
according to president of turkey erdogan it represent turkey civilization and cultural values.
Iran has been the 1st super power in the world. The most powerful empire in mediaeval time was the Persian Empire. At present Iran at its strongest. Iran has the strongest militia in the form of non-state Actors.
India and west asia
West Asia lies in India's extended neighbourhood in the 2nd mandal.
Significance of west Asia for india
West Asia is significant not just for India but is treated as the most sensitive region in geopolitics.
Q. Why
Ans. Since the beginning of modern time west asia has been the place of great games. Means it was never in peace because of continuous involvement of great powers.
Q. Why
Ans. West asia has everything which politics will require to bild
- The greatest importance of west asia lies in its location. Connecting south asia, central asia, europe, north Africa. It connects major markets and the region of resources.
Hence even before the discovery of oil west asia has geopolitical hotspot.
- West asia has been a place of intersection of civilizations, the place of origin of 3 major religions
- Jewish
- Christianity
- Islam
All 3 are abrahamic religions. (politics of religion)
3. at present oil and gas trade further reason for involvement in major power.
West Asia has been one of the earliest regions of engagement of India on world affairs. The very 1st diplomatic position which new delhi had to take was in 1947, when UN was preparing itself for establishment of israel (1948)
India being the 1st non arab country to oppose creation of israel that is why nehru was criticised by the west and trying to the “ more arab than arabs”
West Asia has been the most successful area of India' s diplomacy , historically.
India' s engagement with southeast asia has been much hyped , even today the bilateral trade between india and asian countries despite being in free trade agreement is much less than the bilateral trade and investment which we have with west asia.
West Asia has been the place from where India started its attempt to build counter hegemony. It means building new discourse. Instead of calling the region of middle east India started using the term west asia. The ministry of external affairs describes the region of WANA(West Asia and North Africa)
West Asia is the place for which India has invented its signature idea of foreign policy. Policy of non alignment. Means
- Stay away from great power politics.
- Exercising strategic autonomy
In the regional context of west asia maintain independent bilateral relations, ensuring that the inter state tension among west asian states do not harm India' s interest. India continues to have good relations with all the poles of west asian policies. Be with iran or UAE
West Asia is a place where we exercise our policy of non alignment in a most professional manner. The guiding principle of non alignment have been
- Independent foreign policy
- Stay away from alliance
- Non interference in the domestic affairs
West Asia has been the place for establishing India' s leadership in the 3rd world . Non aligned movement has drawn countries of west asia and Palestinian allows call India To establish its leadership. West Asia has been significant for India's growth and development. According to professor Girijesh pant, west asia is A place not to displace India's power But to augment India's power.
- It is source of india,s Two thirds of India's energy need
- It is home to around 9 million expatriate constituting 60% of their population
- The annual remittances have reached to the level of 80 billion, 56% of the total remittances India received
However managing relations with west asia are not so easy
Q. Why
Ans.
- Involvement of major powers
- Extreme polarisation within the region/international faultlines.
So far we have been successful in navigating choppy water of west asia.
Time to have challenges of west asia to India's security and prosperity are going to increase
Geo strategic significance of west asia.
Because of great power politics, West Asian states are turning into failed states. There is a phenomenal increase in the number of non state actors along with growing radicalisation.
It is to be seen how india will be able to manage the security threats considering the rise of politics of hindutva in india.
Geo political concerns
Geo political concerns mean issues from the perspective of balance of power. The hype of power equations which are Emerging in west asia do not seem to be favourable to india.
Phases
During the Cold War, we managed West Asia Because Russians dominance in the region especially among countries like Iraq, Syria.
After the end of the cold war India could manage because of US dominance in the region and India's improve the relation with US. US has instrumental strengthening India' s relationship with GCC countries. UAE and saudi arabia
Present situation
Geo politics in west asia has become multi-polar. Unfortunately there is a rise of the countries with which india doesn't have good relations
- Increasing influence of china
- Increasing assertiveness with turkey
- The decline of USA
The ray of hope for india is resurgence of Russia Since 2015, russia has increasingly involved itself in west asia
Geo economic concerns
It arises because of China's greater involvement in west Asia and the adversarial relation between India and china.
There is a increasing security threat around sea lines of communication
- Near red sea
- In eastern Mediterranean region (North Africa countries, Libya, Egypt)
The future of the Indian connectivity initiative continues to be uncertain
- International North South Transport Corridor (INSTC)
- IMAC corridor.
Q. What is the conceptual Framework of India with respect to West Asia
Ans. In 2015, pm modi while Inaugurating make in India initiative at New Delhi made a statement “Act East and link west”
Foreign Minister S Jays Sankar at Raisinha dialogue “Look west will meet the ambition of Act East ''. The present political construct with Which India's foreign policy operates in the region is free and open indo Pacific
It means India's West Asian policy will takes into consideration.
- The China factor. The presence of China in Indian Ocean and in West Asia.
- Reviving the legacy of the Raj: (British Ra)
West Asia means the Gulf region and Indian Ocean Of integrated strategic space.
India will be the net security provider to the countries in west asia , east africa, countries in indian ocean and south east Asian.
Maritime security
- Safeguarding the sea lines of communication from non conventional security threads( piracy , non state actors)
- Joint naval exercises
- Greater participation in the navy in diplomatic platforms like the Indian ocean naval symposium.
Q. Explain the emerging geo political scenario in west asia and analyse indian initiatives to manage India' s interest in the region.
Profile of west asia. Or greater middle east.
Segment
- India and iran
- India and GCC countries
Countries of Levant region
- Israel
- Palestine
- Turkey (Greece Cyprus)
- South Caucas region : Georgia Armenia Azerbaijan
- Central Asia
- Afghanistan
Evolution of politics in the Middle east.
Middle east is at the junction of 2 civilizations
- Christian civilizations
- Islamic civilization
Unfortunately they do not have peaceful past.
Samuel p. Huntington, in his book clash of civilization talk about the bloody borders, islam had with his neighbours i.e. europeans
Middle east in mediaeval time.
During this time most of the areas in middle east has been under ottoman Empire. The largest empire spreading in the middle east, central asia, eastern Mediterranean or north africa, southern europe( greece , turkey), Bulgaria (caucus.)
Ottoman Empire, came into conflict with the Byzantine Empire. The eastern part of roman Empire the centre of which was in Constantinople.(Which is now Istanbul)
The influence of Eastern church extended to southern Europe countries and as far as russia ( orthodox church)
Its influence was also on Georgia Armenia Azerbaijan
Home work
(Ions)
The Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS) Explained
The Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS) is a biennial forum for maritime cooperation among the littoral states of the Indian Ocean Region.expand_more It was conceived in 2008 by the Indian Navy and serves as a platform for:
- Discussing regional maritime issues: This includes topics like piracy, illegal fishing, marine pollution, humanitarian assistance, and disaster relief.
- Promoting friendly relationships: IONS encourages dialogue and understanding between member states, fostering trust and cooperation on maritime security matters.expand_more
- Enhancing maritime security cooperation: The forum facilitates joint exercises, information sharing, and capacity building initiatives among member navies.
Here's a summary of key points about IONS:
- Frequency: Biennial meetings (every two years)expand_more
- Membership: Open to all littoral states of the Indian Ocean Region (currently 46 members)exclamation
- Structure: Conclave of Chiefs (CoC) is the highest decision-making body, with Working Groups focusing on specific areas of cooperation.expand_more
- Recent Event: The 8th IONS CoC was held in December 2023 in Bangkok, Thailand.expand_more India is scheduled to take over as Chair in 2025.expand_more
Additional Resources:
- Official Website: https://www.ions.global/
- Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Indian_Ocean_Naval_Symposium
- Press Information Bureau of India (PIB): https://pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetailm.aspx?PRID=1981010
(CSTO) and its member countries
The Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) is an intergovernmental military alliance in Eurasia consisting of six post-Soviet states: Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Tajikistan. It was formed in 2002 with the signing of the Collective Security Treaty, which had been established in 1992.
Opens in a new window
zh.m.wikipedia.org
Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) member states map
The CSTO's main goals are:
- To strengthen peace, international and regional security and stability
- To protect on a collective basis the independence, territorial integrity and sovereignty of the Member States
- To counter terrorism and extremism
- To combat transnational organized crime
- To cooperate in the field of military security
The CSTO has a number of bodies and institutions, including:
- The Collective Security Council, the highest body of the Organization, which consists of the heads of state of the member states
- The Permanent Council, which coordinates the Organization's activities between sessions of the Collective Security Council
- The Secretariat, which provides administrative and technical support to the Organization
- The Collective Security Forces, which consist of military contingents from all member states
The CSTO has been involved in a number of activities, including:
- Conducting joint military exercises
- Deploying peacekeeping missions
- Providing military assistance to member states
- Countering terrorism and extremism
The CSTO has been criticized for being a tool of Russian foreign policy and for its lack of transparency. However, it has also been praised for its role in promoting stability in Central Asia and for its efforts to counter terrorism and extremism.
Here are some additional details about the CSTO:
- Headquarters: Moscow, Russia
- Secretary General: Stanislav Zas
- Official languages: Russian
- Website: https://en.odkb-csto.org/
Ashgabat Agreement
The Ashgabat Agreement, also known as the Agreement on International Transport and Transit Corridor, is a multimodal transport agreement established to facilitate trade and transit between Central Asia and the Persian Gulf. Here's a breakdown:
Key Points:
- Signatories: Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Iran, India, Pakistan, and Oman
- Established: 2011, entered into force 2016
- Objective: Create a land and sea trade route connecting Central Asian countries with the ports of Iran and Oman.
- Benefits:
- Reduced transportation costs and time for goods
- Increased trade opportunities for member countries
- Enhanced regional economic integration
- Improved connectivity within the Eurasian region
Details:
- The agreement establishes a designated transport corridor through the participating countries, utilizing various modes like road, rail, and sea.
- It aims to simplify customs procedures and facilitate the movement of goods across borders.
- The agreement also encourages infrastructure development along the corridor, such as new roads and ports.
- India joined the agreement in 2018, seeking to diversify its trade routes with Central Asia and access new markets.
Additional Resources:
- Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ashgabat_Agreement
- India's Ministry of External Affairs: [invalid URL removed]
- IDSA Analysis: [invalid URL removed]
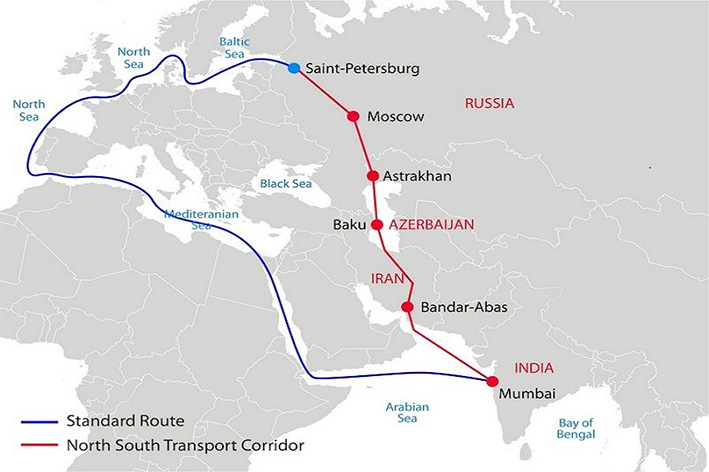
International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC)
The International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) is a crucial project aimed at enhancing trade connectivity between India, Iran, Azerbaijan, Russia, Central Asia, and Europe. Here's a detailed overview:
What is INSTC?
- A 7,200-kilometer multi-modal network of sea, rail, and road routes for moving freight across Eurasia.
- Connects major cities like Mumbai, Moscow, Tehran, Baku, Bandar Abbas, and Astrakhan.
- Aims to provide an alternative to the traditional Suez Canal route, offering:
- Reduced transit times: By 40%, potentially decreasing journey duration from 45-60 days to 25-30 days.
- Lower freight costs: Estimated 30% reduction compared to the Suez Canal route.
Key Features:
- Established in 2000, ratified by India, Iran, and Russia in 2002.
- Currently includes 13 member countries, with Bulgaria as an observer.
- Project cost estimated at $620 million, funded by member governments and organizations like Asian Development Bank (ADB).
- Offers potential for passenger travel in the future.
Current Status:
- Operational but still under development.
- Facing challenges like infrastructure gaps, border procedures, and geopolitical complexities.
- Several sections are operational, including:
- Chabahar port in Iran, crucial for India's access to Central Asia and Europe.
- North-South Transnational Corridor, spanning Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, and Iran.
Significance:
- Potential to boost trade and economic cooperation between member countries.
- Offers India access to Central Asian markets and reduces dependence on traditional trade routes.
- Geopolitical importance for Russia and Iran as an alternative to Western-dominated corridors.
Additional Resources:
- Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/International_North%E2%80%93South_Transport_Corridor
- Ministry of External Affairs, India: https://fsi.mea.gov.in/lok-sabha.htm?dtl/37388/QUESTION+NO1085+INTERNATIONAL+NORTHSOUTH+TRANSPORT+CORRIDOR
- Backgrounder: International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC), Geopolitical Monitor: https://southasianvoices.org/geopolitics-of-the-north-south-transport-corridor/